
- #HOW TO VIEW VBA IN EXCEL 2016 HOW TO#
- #HOW TO VIEW VBA IN EXCEL 2016 CODE#
- #HOW TO VIEW VBA IN EXCEL 2016 PLUS#
In this case, we are going to select manually the data range "Extended Properties=""Excel 12.0 Xml HDR=YES"" " '- Declare Variables to store the connection, the result and the SQL queryĭim connection As Object, result As Object, sql As String, recordCount As Integer

The following example, will use the mentioned logic to connect to the current spreadsheet and will query the range A1:E6 (selecting the whole table in the example excel) and will print every row in the immediate window: Sub MyMethod()
You will use this connection to run the SQL. HDR=Yes : indicates that the first row contains the column names, not data.ConnectionString: we will use the current excel file as the database.Provider: we will use the Microsoft Access Database Engine 2010 (.12.0).The connection properties are described as follows: "Extended Properties=""Excel 12.0 Xml HDR=NO"" " ConnectionString = "Data Source=" & ThisWorkbook.Path & "\" & ThisWorkbook.Name & " " & _ Set connection = CreateObject("ADODB.Connection") '- Connect to the current datasource of the Excel file
#HOW TO VIEW VBA IN EXCEL 2016 HOW TO#
You need to understand how to connect to the workbook data source that will be handled with the following code: Dim connection As Object
#HOW TO VIEW VBA IN EXCEL 2016 CODE#
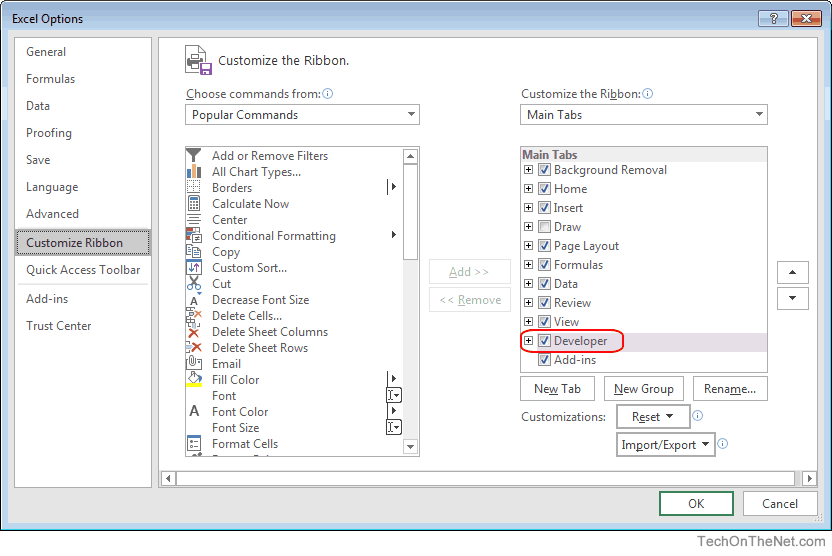
In this example, we are going to work with plain code and will run them independently to test them. In the Visual Basic window, open the code window of your sheet and let's type some code! According to your needs you may create a custom macro and assign them to the action of buttons or other kind of stuff. In this new interface you will be able to run your VB code. In this tab, launch the Visual Basic window: You can do this easily opening the Excel options (File > Options) and searching for the Customize Ribbon tab, in this Tab you need to check the Developer checkbox to enable it in your regular interface:Ĭlick on Ok and now you should be able to find the Developer tab on your excel ribbon. In order to launch the window of Visual Basic to run some code on your spreadsheets, you will need to enable the Developer tab on the excel Ribbon. Launch Microsoft Visual Basic For Applications In this article, I will explain you from scratch how to use Microsoft Visual Basic for Applications to develop your own macros and run some SQL queries against plain data in your excel spreadsheets. Of course, finding such information as a regular user is quite easy and simple using filters and so, however the assignment requires to do the queries using SQL and Visual Basic for the job. Which users were born in 2010 and were ranked in place #1.Which users are boys and live in Boston.

The goal of this task is to write raw SQL Queries against the available data in the spreadsheet to find the answer of the following questions:
#HOW TO VIEW VBA IN EXCEL 2016 PLUS#
For example, for this article, we are going to use the following Sheet in Excel Plus 2016: Instead of a database, we are going to query plain data from an excel spreadsheet (yeah, just as it sounds). For this assignment, it's necessary to find the answer or data as response of a query. If the Project Explorer is not visible when you open the Microsoft Visual Basic for Appliations window, you can make it visible by selecting Project Explorer under the View menu.In the last days, I received an unusual request from a friend that is working on something curious because of an assignment of the University. Whereas, the code within an Excel object is typically only used by that object. The VBA code in Module1 can used anywhere in your spreadsheet. In this example, there are four Excel objects which represent each sheet and workbook in your Excel file - Sheet1, Sheet2, Sheet3, and ThisWorkbook. It is a hierarchical listing of the objects recognized by VBA. The Project Explorer can usually be found in the top left portion of the Microsoft Visual Basic window. Next, let's take a few moments to analyze the various sections in the Microsoft Visual Basic window. The Microsoft Visual Basic for Applications window displays your VBA environment in Excel 2016:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
